Overview
Kinetica provides two means of backing up data:
- Database Backup - full, incremental, & differential data hot backup
- System Backup - file-based full system backup
Database Backup
SQL commands can be used to initiate hot backups, with full, incremental, & differential snapshots, and restorations of schema objects & data within the database.
| Objects Backed Up | Objects Not Backed Up |
|---|---|
Note
- For the set of SQL commands for database backup, see Database Backup/Restore.
- For a full system backup, see System Backup.
Snapshot Types
Three types of snapshots are supported for database objects & data:
- full - snapshot of the given database objects & data
- incremental - snapshot of the changes in the database objects & data since the last snapshot of any kind
- differential - snapshot of the changes in the database objects & data since the last full snapshot
Backup Storage
Database backup files will be transferred to the target specified in the given data sink. There, they will be stored under two levels of directories: the top-level directory will be the name of the database backup and the subdirectory will be the timestamp the snapshot was taken; e.g.:
/<backup_name>/ki_backup_info.json /<backup_name>/<backup_name>.mdb /<backup_name>/<snapshot_timestamp>/<snapshot_timestamp>.mdb /<backup_name>/<snapshot_timestamp>/rank-<rank_number>/tom-<TOM_number>/*
A new backup will result in the creation of a directory with the corresponding backup name, as well as a snapshot timestamp directory with the full snapshot files. An incremental or differential snapshot for a given backup will result in the creation of another snapshot timestamp directory, under the backup directory, containing all the files for that snapshot.
A data source is required to retrieve detail about backups and restore database objects & data from them. The data source must point to the same remote store as the data sink through which a backup was created in order to access and restore from it.
Backup Use Case
A typical usage of the backup feature is:
- create a backup, taking an initial full snapshot
- schedule iterative incremental or differential snapshots
- restore a backup
Initial Backup
To create the initial backup, run a CREATE BACKUP statement, in SQL, that specifies:
- the name to use for the backup--the backed-up database object set
- the data sink that will be used to transfer the backed-up files to the remote store (e.g., s3)
- the set of database objects to back up
For example, to create an initial backup with the following parameters:
- daily_backup - name of the backup
- backup_ds - data sink targeting the remote file service
- example_backup - name of the schema to back up
| |
Schedule Iterative Snapshots
To schedule iterative snapshots after the initial backup is done, create a SQL procedure that specifies:
- the name of the backed-up database object set (same as the initial backup)
- the data sink that will be used to transfer the snapshots to the remote store (same as the initial backup)
- the schedule for running the incremental snapshots
For example, to schedule incremental snapshots with the following parameters:
- daily_backup - name of the backup to which snapshots will be added
- backup_ds - data sink targeting the remote file service
- 1 DAY - daily snapshot interval
- STARTING AT...2025-01-01 - starting at a date in the past causes the first snapshot to be taken at the next possible time interval
- STARTING AT...00:00:00 - schedule the snapshot to be taken at midnight
| |
Restore Backup
To restore database objects and table data from the latest snapshot in a backup, using the following parameters:
- daily_backup - name of the backup to restore
- restore_ds - data source targeting the remote file service
- example_backup - name of the schema to restore
- replace - any exising database object will be overwritten by its counterpart from the backup
| |
System Backup
You can back up Kinetica data through Workbench. Backups can be used to perform a complete data restoration from the point in time the backup was taken. A backup can be requested while the cluster is in a running state; there is no need to suspend it first. Restoring data from a backup, on the other hand, does require the cluster to be suspended first.
Clicking on Snapshots, will display two lists:
- Activity - Backup jobs that either are in progress or have failed (not shown if none are in either state)
- Backups - Completed backups, ready to be used to restore the cluster
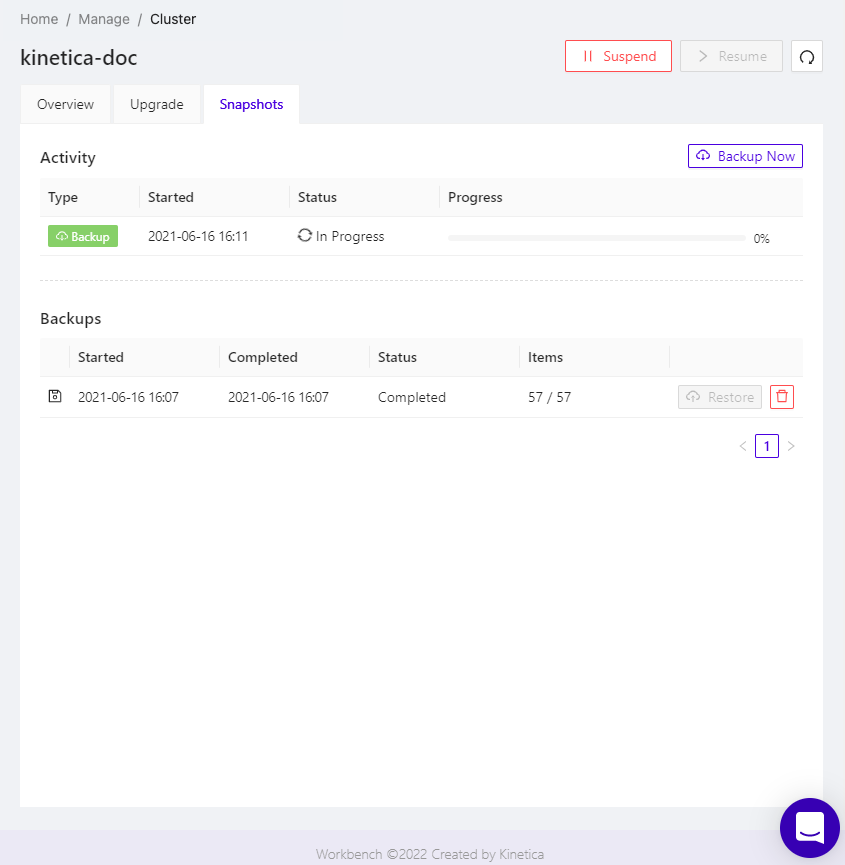
To perform a complete backup of all data in the cluster, click Backup Now.
To cancel an in-progress or failed backup, click the Cancel for that job's entry in the list.
To perform a complete restoration of all data from a snapshot, click the Restore for that backup's entry in the list, making sure the cluster has been suspended first. To delete a given backup, click its associated trash can icon.